What is 5G?
5G is the 5th generation of mobile networks, a significant evolution from the 4G networks.
5G is designed to meet the very large growth in data and connectivity of today’s modern society, the internet of things with billions of connected devices, and tomorrow’s innovations. 5G initially operated in conjunction with existing 4G networks before evolving to fully standalone networks. The rollout of 5G has helped meet Australians’ growing demand for more data, with the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) reporting that between 2023 and 2024 the volume of data downloaded by mobile services increased by 33% and this is set to continue.
What does 5G enable?
5G has enabled enhanced mobile broadband, bringing instantaneous connectivity to billions of devices, the Internet of Things (IoT) and a truly connected world. For communities, 5G enables real-time connection of billions of devices to provide a safer and more efficient place to live.
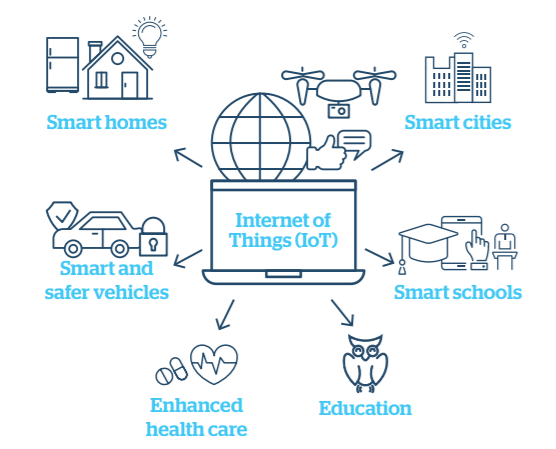
For businesses and industry, 5G and IoT provides a wealth of data, allowing them to gain insights into their operations like never before. Businesses operate and make key decisions driven by data (e.g. parcel tracking), and innovate in different application areas including agriculture, smart farms and manufacturing. This provides cost savings, better customer experience and long-term growth.
What was the first applications for 5G?
5G-enabled products such as wireless broadband, mobile devices and IoT were the first applications using 5G.
What do 5G devices offer?
The prime benefits of 5G devices are significantly faster speeds in data access, downloading and streaming content. In addition, 5G devices have increased computing power and make use of faster connectivity, meaning that the devices enjoy virtually instantaneous connections to the network,
as well as greater connectivity when on the move. 5G enables applications such as remote monitoring, automation of production, medical monitoring and even remote surgery
How does 5G work?
5G delivers faster speeds, better response times and greater capacity. 5G networks are designed to work in conjunction with 4G networks using a range of macro cells, small cells and dedicated in-building systems.
Small cells are a feature of 5G networks and have evolved to include the use of millimetre wave (mmWave) frequencies. Small cells are mini base stations designed for very localised coverage typically from 10 metres to a few hundred metres providing in-fill for the larger macro network. Small cells are essential for the 5G networks.
For more information have a look at our Fact Sheets
Other useful links and information
EMF Explained (AMTA, GSMA, MWF)
